CALCIUM with MAGNEISUM, ZINC, VITAMIN D3 & CISSUS QUADRANGULARIS, 60 Tablets
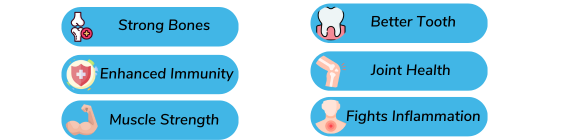
- Nourishes strong bones: Our product is formulated with a potent blend of calcium, magnesium, and zinc, which work together to nourish your bones. By supporting bone-building cells, our product helps promote healthy bone regeneration, enhances mineral retention, and reduces the risk of bone fractures.
- Power of cissus: Our calcium, magnesium, and zinc supplement includes Cissus Quadrangularis, a powerful herb with restorative properties. It helps support joint health, reduce joint pain, and improve mobility. By promoting joint health, our supplement can help you stay active and enjoy an active lifestyle.
- Supports immune health: Our calcium and mineral supplement provides a natural boost to your immune system. Our product contains magnesium and zinc, both of which are essential for the proper functioning of your immune cells. By supporting your immune system, our supplement can help you maintain optimal energy levels throughout the day.
- Promotes muscle function: Our unique formula is designed to maintain muscle strength and function. With its anti-inflammatory properties, it helps reduce muscle soreness and promotes tissue repair. Our product also provides the essential nutrients needed for optimal muscle performance.
- Enhances bone density: Our product is specially formulated to improve bone density and prevent bone loss. By providing essential nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and zinc, our supplement helps to strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures.
Net Qty: 60 Tablets
MRP ₹: 599, USP ₹ Per Tablet: 09.98
Country of Origin: INDIA
Out of stock
Offers
₹599.00 ₹149.00
Out of stock
Category Letter Vitamins




FSSAI APPROVED

USFDA REGISTERED

GMP CERTIFIED

ISO CERTIFIED

MAKE IN INDIA
Active Ingredients

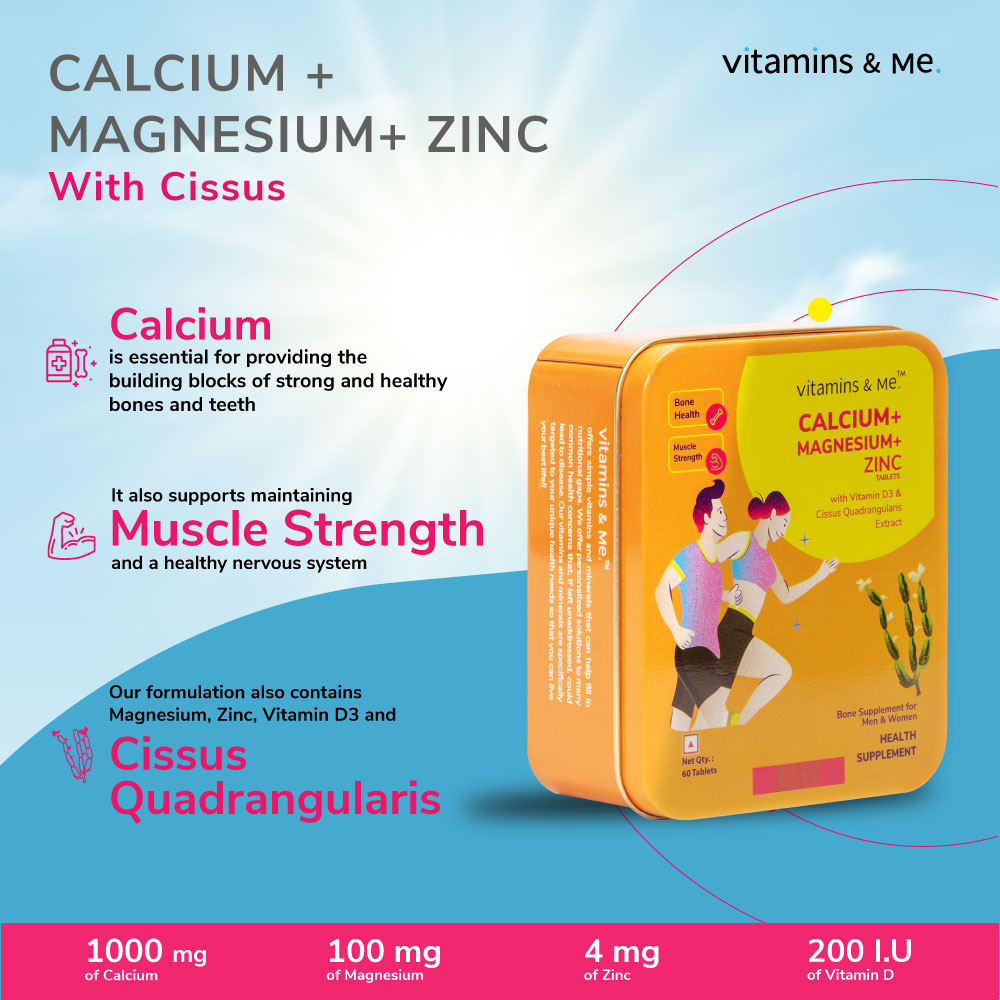
Calcium
Calcium Citrate Malate 1000 mg

Magneisum
Magneisum 100 mg

Zinc
Zinc 4 mg

Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) 200 IU

Cissus Quadrangularis
Cissus Quadrangularis Linn Extract 50 mg
SCIENTIFIC EVIDENCE
POWER OF CISSUS
CALCIUM INTAKE IN INDIA
MAGNESIUM-ZINC-CALCIUM-VITAMIN D CO-SUPPLEMENTATION
POWER OF CISSUS
Cissus quadrangularis is a medicinal plant that has been traditionally used for its various therapeutic properties. Research studies have shown that this plant has numerous health benefits, making it a popular ingredient in many dietary supplements.
One of the main benefits of Cissus quadrangularis is its ability to promote bone health. Several studies have demonstrated that Cissus quadrangularis can help improve bone mineral density and reduce the risk of fractures. For example, a double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that supplementation with Cissus quadrangularis significantly increased bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (1).
In addition to its effects on bone health, Cissus quadrangularis has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Several studies have demonstrated that Cissus quadrangularis can help reduce inflammation and pain associated with various conditions, including arthritis and exercise-induced muscle damage (2, 3).
Moreover, Cissus quadrangularis has been found to have antioxidant properties. Research studies have shown that Cissus quadrangularis can help reduce oxidative stress and protect against cellular damage caused by free radicals (4).
Overall, Cissus quadrangularis is a promising medicinal plant that has a wide range of health benefits. Its ability to improve bone health, reduce inflammation, and provide antioxidant protection makes it a valuable ingredient in many dietary supplements.
References:
1. Potu BK, et al. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(6):803-10. doi: 10.1007/s00774-009-0102-0. Epub 2009 Jun 23. PMID: 19548018.
2. Oben J, et al. Phytother Res. 2008 Sep;22(9):1142-7. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2400. PMID: 18510884.
3. Kusamran WR, et al. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011 Aug;94 Suppl 7:S110-6. PMID: 22043697.
4. Suntar I, et al. Pharm Biol. 2010 Nov;48(11):1264-72. doi: 10.3109/13880200903527758. PMID: 20954862.
One of the main benefits of Cissus quadrangularis is its ability to promote bone health. Several studies have demonstrated that Cissus quadrangularis can help improve bone mineral density and reduce the risk of fractures. For example, a double-blind, placebo-controlled study found that supplementation with Cissus quadrangularis significantly increased bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (1).
In addition to its effects on bone health, Cissus quadrangularis has also been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Several studies have demonstrated that Cissus quadrangularis can help reduce inflammation and pain associated with various conditions, including arthritis and exercise-induced muscle damage (2, 3).
Moreover, Cissus quadrangularis has been found to have antioxidant properties. Research studies have shown that Cissus quadrangularis can help reduce oxidative stress and protect against cellular damage caused by free radicals (4).
Overall, Cissus quadrangularis is a promising medicinal plant that has a wide range of health benefits. Its ability to improve bone health, reduce inflammation, and provide antioxidant protection makes it a valuable ingredient in many dietary supplements.
References:
1. Potu BK, et al. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(6):803-10. doi: 10.1007/s00774-009-0102-0. Epub 2009 Jun 23. PMID: 19548018.
2. Oben J, et al. Phytother Res. 2008 Sep;22(9):1142-7. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2400. PMID: 18510884.
3. Kusamran WR, et al. J Med Assoc Thai. 2011 Aug;94 Suppl 7:S110-6. PMID: 22043697.
4. Suntar I, et al. Pharm Biol. 2010 Nov;48(11):1264-72. doi: 10.3109/13880200903527758. PMID: 20954862.
CALCIUM INTAKE IN INDIA
Data collected from National Nutrition Monitoring Bureau (NNMB) on nutritional status of rural, tribal and urban populations in 10 out of 32 Indian states and union territories from 1975 to 2017 showed there was a decline in dietary intake of calcium both in rural and tribal population in the past four and a half decades.
References
Harinarayan, C.V., Akhila, H., 2019. Modern India and the Tale of Twin Nutrient Deficiency–Calcium and Vitamin D–Nutrition Trend Data 50 Years-Retrospect, Introspect, and Prospect. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00493
References
Harinarayan, C.V., Akhila, H., 2019. Modern India and the Tale of Twin Nutrient Deficiency–Calcium and Vitamin D–Nutrition Trend Data 50 Years-Retrospect, Introspect, and Prospect. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2019.00493
MAGNESIUM-ZINC-CALCIUM-VITAMIN D CO-SUPPLEMENTATION
A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was performed to assess the effects of Magnesium-Zinc-Calcium-Vitamin D Co-supplementation on endocrine, inflammation, and oxidative stress biomarkers in vitamin D-deficient women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). The results showed that co-supplementation for 8 weeks among vitamin D-deficient women with PCOS had beneficial effects.
References
Maktabi, M., Jamilian, M., Asemi, Z., 2018. Magnesium-Zinc-Calcium-Vitamin D Co-supplementation Improves Hormonal Profiles, Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biol Trace Elem Res 182, 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1085-0
References
Maktabi, M., Jamilian, M., Asemi, Z., 2018. Magnesium-Zinc-Calcium-Vitamin D Co-supplementation Improves Hormonal Profiles, Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biol Trace Elem Res 182, 21–28. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-017-1085-0

NON-GMO

GLUTEN FREE

HALAL

NO EGG

DAIRY FREE
Important to know
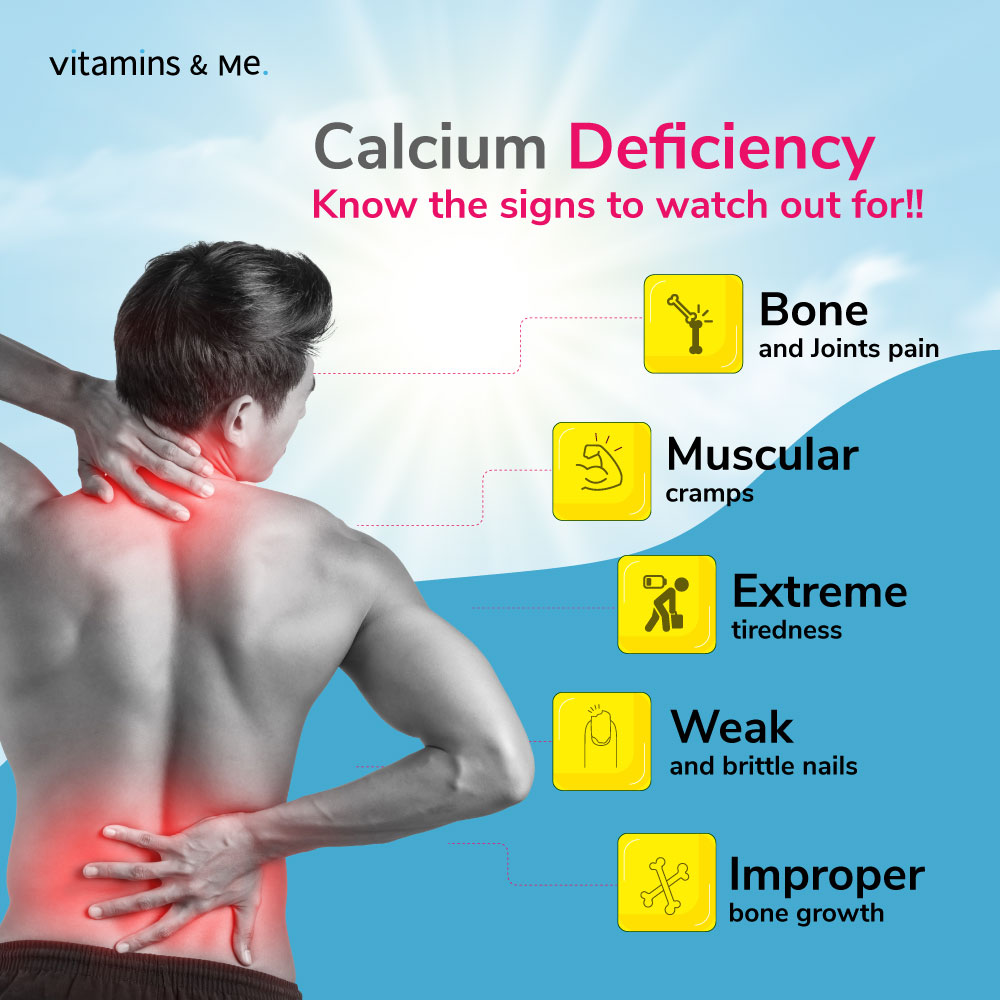
• Weak bones and muscles.
• Increased risk of fractures.
• Impaired immune function
• Increased risk of fractures.
• Impaired immune function
For adults: Take One Tablet in a day or as recommended by Healthcare professional

Trusted by over 10000+ Clients worldwide since 2020
4.6
4.6/5
Formulated by Pharmacists
Related products
-
Sale!
 Out of stock
Letter Vitamins
Out of stock
Letter VitaminsOMEGA 3 BURPLESS FISH OIL 1000 MG with 180 MG EPA & 120 MG DHA 40 Softgels
₹699.00₹299.00 -
Sale!
 Out of stock
Out of stock
-
Sale!
 Out of stock
Out of stock